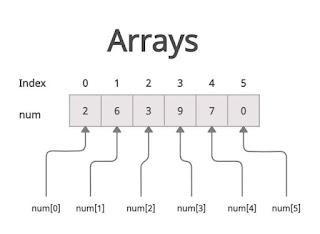
Array is nothing but store more than one value at a time .
ex:
int a[5] ,char ch[10], long num[5], etc….
Array is a collection of similar data types in which each element is unique one and located in a separate memory location .
Array has a fixed size.
Array elements are contiguous memory locations .
NULL character = ‘\0’.
One Dimensional Array
Two Dimensional Array
Three or Multidimensional Array
One Dimensional Array
The elements of an integer array a[5] stored contiguous memory location .
Write a program to display character array with their address
#include<stdio.h>void main (){
char name[10]= {'A','R','R','A','Y'};
int i=0;
printf("character memory location \n ");
while(name[i]!='\0'){
printf("\n[%c]\t\t [%u]",name[i],& name[i]);
i++;
}
}
character memory location
[A] [6684178]
[R] [6684179]
[R] [6684180]
[A] [6684181]
[Y] [6684182]
Write a program to display the contents of two arrays .The 1st array should contain the string and 2nd numerical numbers .
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
char city[6] = {'N','A','N','D','E','D'};
int i,pin[6] = {4,3,1,6,0,6};
for(i=0;i<6 i="" stdio=""> <6;i++)printf("%c",city[i]);
printf(" - ");
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
printf("%d",pin[i]);
}Output :
NANDED - 431606
Two dimensional Array
Two dimensional array can be thought of as a rectangular display of elements with rows and columns .
For ex - x[3][3].
Write a program to display the elements the two dimensional Array .
#include<stdio.h>
void main (){
int i,j;
int a[3][3] = { {1,2,3},{4,5,6},{6,7,8}};
printf("The elements of an array \n\n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%5d",a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
Output :
The elements of an array
1 2 3
4 5 6
6 7 8
Write a program to perform addition and subtraction of two matrices whose orders are up to 10 *10
#include<stdio.h>
void main (){
int i,j,r,c,a[10][10],b[10][10];
printf("enter the matrix of order A and B up to 10 X 10:");
scanf("%d %d",&r,&c); printf("enter the element of matrix A\n");
for(i=0;i<r;i++){
for(j=0;j<c;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
printf("enter the element of matrix B\n");
for(i=0;i<r;i++){
for(j=0;j<c;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n matrix Addition \n");
for(i=0;i<r;i++){
for(j=0;j<c;j++)
printf("%5d",a[i][j]+b[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n matrix Substraction \n");
for(i=0;i<r;i++){
for(j=0;j<c;j++)
printf("%5d",a[i][j]-b[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
getche();
}
Output :
enter the matrix of order A and B up to 10 X 10:3 3
enter the element of matrix A
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
enter the element of matrix B
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
matrix Addition
2 4 6
8 10 12
14 16 18
matrix Substraction
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0